How to use DAX RELATED Function in Power BI
The RELATED Function Returns a related value from another Related table. The RELATED function requires that a relationship exists between the current table and the Related table with related information.
We can specify the column that contains the data that we want, and the function follows an existing Many-to-One relationship to fetch the value from the specified column in the related table. If a relationship does not exist, you must create a relationship.
When the RELATED function performs a lookup, it examines all values in the specified table regardless of any filters that may have been applied.
Defining a new Column and a new Measure on the 'Products_One' Table :
Products_One[Unit_Price]*RELATED(SalesByCust_One[Units_Sold])
m_TotalSales =
SUMX(Products_One,
Products_One[Unit_Price]*RELATED(SalesByCust_One[Units_Sold])
)
We were able to define the similar new Column and a Measure successfully on any one of the tables.
Note:
In real time, we should define them only in any one of the Table, otherwise we may get a Circular reference error when try to define same calculated Columns with same reference on both the tables, in case of One-to-One Relationship.
Now we can see all these new Columns and Measures will returns the same values as follows.
The RELATED Function Returns a related value from another Related table. The RELATED function requires that a relationship exists between the current table and the Related table with related information.
We can specify the column that contains the data that we want, and the function follows an existing Many-to-One relationship to fetch the value from the specified column in the related table. If a relationship does not exist, you must create a relationship.
When the RELATED function performs a lookup, it examines all values in the specified table regardless of any filters that may have been applied.
Notes:
It works like an Excel Vlookup Function.
It works on the Models with a One-to-One Relationship and Many-to-One Relationship as well.
In case of One-to-One Relationships, It can be used in the new Column/Measure defined on any One-Side table to perform the Lookup & retrieve the values from other Related table.
But in case of Many-to-One / One-to-Many Relationships, It can be used in a new Column /Measure defined only on Many-Side table to perform the Lookup & retrieve values from the One-Side table.
Basic Syntax:
RELATED(Table[Column])
Now will discuss about the Functional behavior of the RELATED Function in One-to-One and One-to-Many / Many-to-One relationships.
1) One-to-One Relationship:
Suppose we have two Tables with One-to-One Relationship in a Power BI Model as follows.
For better understanding of the Relationship, I just added suffix as "_One" , tells that the tables have the One-to-One relationship.
Since both tables have the One-to-One relationship based on the key "Prod_Id", we can see the Unique rows for the Prod_Id in both the tables.
This means the column "Prod_Id" in one table has only one instance of a particular value, and the other related table has only one instance of a particular value.
Since there was One-to-One Relationship between the Tables, we can use the RELATED Function to Calculate a New Column/Measure defined on any one of the One-Side table to perform the Lookup & retrieve the values from other Related table.
Defining a new Column and a new Measure on the 'SalesByCust_One' Table :
Defining a new Column and a new Measure on the 'SalesByCust_One' Table :
cTotalSales =
SalesByCust_One[Units_Sold]*RELATED(Products_One[Unit_Price])
SalesByCust_One[Units_Sold]*RELATED(Products_One[Unit_Price])
mTotalSales =
SUMX(SalesByCust_One,
SalesByCust_One[Units_Sold]*RELATED(Products_One[Unit_Price])
)
SUMX(SalesByCust_One,
SalesByCust_One[Units_Sold]*RELATED(Products_One[Unit_Price])
)
Products_One[Unit_Price]*RELATED(SalesByCust_One[Units_Sold])
m_TotalSales =
SUMX(Products_One,
Products_One[Unit_Price]*RELATED(SalesByCust_One[Units_Sold])
)
We were able to define the similar new Column and a Measure successfully on any one of the tables.
Note:
In real time, we should define them only in any one of the Table, otherwise we may get a Circular reference error when try to define same calculated Columns with same reference on both the tables, in case of One-to-One Relationship.
2) One-to-Many Relationship:
Now lets make a Change in a Table "SalesByCust_One", by adding additional records with repeated Product_Ids, and will rename the Table name as "SalesByCust_Many".
Here, we will leave the "Products_One" table as it is without making any changes.
First go to Edit Queries and Select and Rename the Table to "SalesByCust_Many".
Next go to Query Settings > Applied Steps and then click on the Source gear icon.
Once click on the Source gear icon, it will open a window to update the Table.
Now add the more rows to the Table then click OK to apply and save changes to the Table.
When you Apply Changes and Closes the Query Editor window, Immediately we will see the following Error Message, as it is violating the One-to-One relationship already existed.
Now closing this Message Box, then go ahead and change relationship between the Tables from One-to-One to One-to-Many as follows.
Next say OK, then Apply changes.
Now In the One-to-Many / Many-to-One relational Model, we can see that the RELATED Function is working only in the Calculations (new Column/Measures) made on the Many- side table.
cTotalSales =
SalesByCust_Many[Units_Sold]*RELATED(Products_One[Unit_Price])
mTotalSales =
SUMX(SalesByCust_Many,
SalesByCust_Many[Units_Sold]*RELATED(Products_One[Unit_Price])
)
SUMX(SalesByCust_Many,
SalesByCust_Many[Units_Sold]*RELATED(Products_One[Unit_Price])
)
Result:
---------------------------------------------------------------
Notes:
As long as the Relationships flows in Model like, 1: M => 1:M OR 1:M => 1:1, the RELATED function will work fine in the following Scenarios:
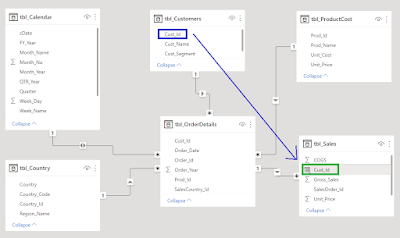
Retrieving the Cust_Id from the Indirect related table tbl_Customers into the tbl_Sales.
Scenario 1:
Relationship Cardinality:
tbl_Customers (1): (M) tbl_OrderDetails (1): (M) tbl_Sales
Relation Keys:
Relationship Cardinality:
tbl_Customers (1): (M) tbl_OrderDetails (1): (1) tbl_Sales
---------------------------------------------------------------
In the following Scenario, the RELATED Function will not work:
Scenario 1:
Relationship Cardinality:
tbl_Customers (1): (M) tbl_OrderDetails (M): (1) tbl_Sales
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Thanks, TAMATAM ; Business Intelligence & Analytics Professional
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------





























No comments:
Post a Comment
Hi User, Thank You for visiting My Blog. If you wish, please share your genuine Feedback or comments only related to this Blog Posts. It is my humble request that, please do not post any Spam comments or Advertising kind of comments, which will be Ignored.